
1Z0-071 Exam Questions & Answers
Exam Code: 1Z0-071
Exam Name: Oracle Database 12c SQL
Updated: Nov 12, 2024
Q&As: 415
At Passcerty.com, we pride ourselves on the comprehensive nature of our 1Z0-071 exam dumps, designed meticulously to encompass all key topics and nuances you might encounter during the real examination. Regular updates are a cornerstone of our service, ensuring that our dedicated users always have their hands on the most recent and relevant Q&A dumps. Behind every meticulously curated question and answer lies the hard work of our seasoned team of experts, who bring years of experience and knowledge into crafting these premium materials. And while we are invested in offering top-notch content, we also believe in empowering our community. As a token of our commitment to your success, we're delighted to offer a substantial portion of our resources for free practice. We invite you to make the most of the following content, and wish you every success in your endeavors.

Download Free Oracle 1Z0-071 Demo
Experience Passcerty.com exam material in PDF version.
Simply submit your e-mail address below to get started with our PDF real exam demo of your Oracle 1Z0-071 exam.
![]() Instant download
Instant download
![]() Latest update demo according to real exam
Latest update demo according to real exam
* Our demo shows only a few questions from your selected exam for evaluating purposes
Free Oracle 1Z0-071 Dumps
Practice These Free Questions and Answers to Pass the Oracle Database Exam
Examine thee statements Which execute successfully:
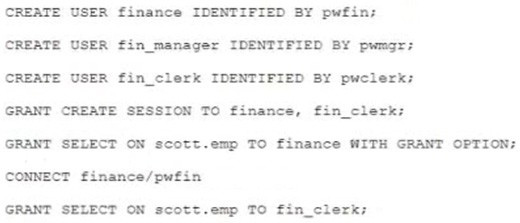
Which two are true? (Choose two.)
A. User FIN_CLERK can grant SELECT on SCOTT.EMP to user FIN_MANAGER.
B. Dropping user FINANCE will automatically revoke SELECT on SCOTT.EMP from user FIN_CLERK.
C. User FINANCE can grant CREATE SESSION to user FIN_MANAGER.
D. Revoking SELECT on SCOTT.EMP from user FINANCE will also revoke the privilege from user FIN_CLERK.
E. User FINANCE is unable to grant all on SCOTT.EMP to FIN_MANAGER.
The SALES table has columns PROD_ID and QUANTITY_SOLD of data type NUMBER.
Which two queries execute successfully?
A. SELECT COUNT(prod_id) FROM sales WHERE quantity_sold>55000 GROUP BY prod_id;
B. SELECT prod_id FROM sales WHERE quantity_sold> 55000 GROUP BY prod_id HAVING COUNT(*)> 10;
C. SELECT COUNT(prod_id) FROM sales GROUP BY prod_id WHERE quantity_sold> 55000;
D. SELECT prod_id FROM sales WHERE quantity_sold> 55000 AND COUNT(*)> 10 GROUP BY COUNT(*)> 10;
E. SELECT prod_id FROM sales WHERE quantity_sold> 55000 AND COUNT(*)> 10 GROUP BY prod_id HAVING COUNT(*)> 10;
Which three statements are true about sequences in a single instance Oracle database? (Choose three.)
A. A sequence's unallocated cached values are lost if the instance shuts down.
B. A sequence number that was allocated can be rolled back if a transaction fails.
C. A sequence can only be dropped by a DBA.
D. A sequence can issue duplicate values.
E. Sequences can always have gaps.
F. Two or more tables cannot have keys generated from the same sequence.
Which two are true about savepoints? (Choose two.)
A. After issuing a savepoint, you can roll back to the savepoint name within the current transaction.
B. They make uncommitted updates visible to sessions owned by other users.
C. You can commit updates done between two savepoints without committing other updates in the current transaction.
D. A ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT command issued before the start of a transaction results in an error.
E. They make uncommitted updates visible to other sessions owned by the same user.
F. After issuing a savepoint, you cannot roll back the complete transaction.
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of CUSTOMERS table.
Using the CUSTOMERS table, you need to generate a report that shows an increase in the credit limit by 15% for all customers. Customers whose credit limit has not been entered should have the message "Not Available" displayed.
Which SQL statement would produce the required result?
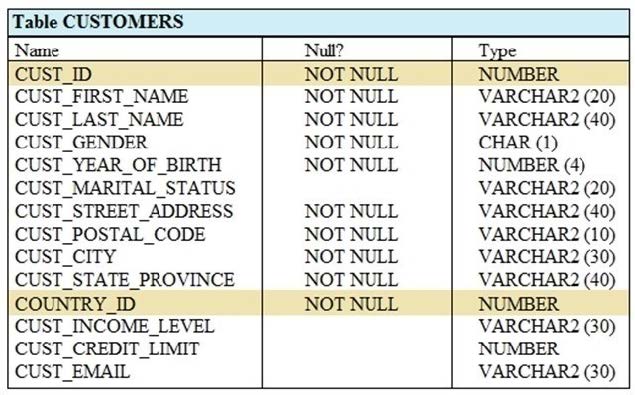
A. SELECT NVL (TO CHAR(cust_credit_limit * .15), 'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
B. SELECT TO_CHAR (NVL(cust_credit_limit * .15), 'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
C. SELECT NVL(cust_credit_limit * .15), 'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
D. SELECT NVL(cust_credit_limit), 'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
Viewing Page 1 of 3 pages. Download PDF or Software version with 415 questions

